Updates to GitHub Importer and the deprecation of the Source Import REST API Endpoint
GitHub Importer is a tool that quickly imports source code repositories, including commits and revision history, to GitHub.com. As part of this release, GitHub Importer has implemented a new method for git source migration that will provide users with improved reliability and more detailed error handling when migrating git source repositories to GitHub. Click here to import your project to GitHub.
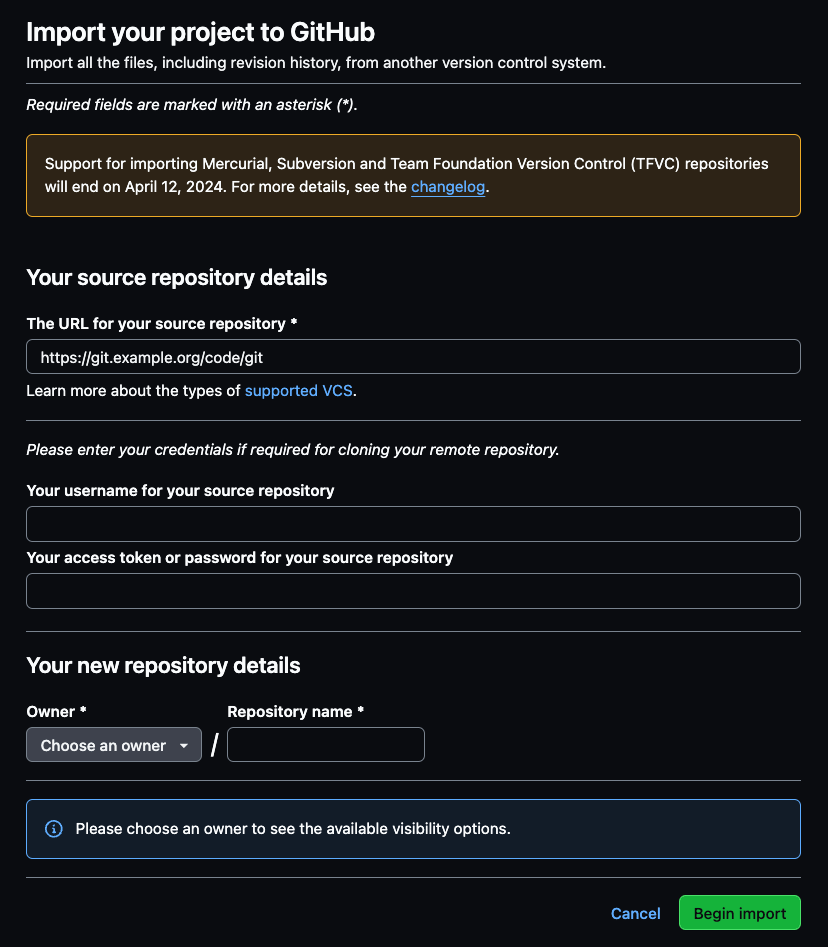
As previously communicated, this change comes with the ending of support for the REST API endpoints for source imports. Moving forward, these endpoints will return an error. Users are encouraged to make use of the new import repository page instead.
Lastly, we previously announced that GitHub Importer will no longer support importing Mercurial, Subversion and Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) repositories. Effective today, we’ve ended support for this functionality due to extremely low levels of usage. Moving from these alternative version control systems to Git is simple thanks to fantastic open source tools – for more details, read our Docs article, “Using the command line to import source code”.
